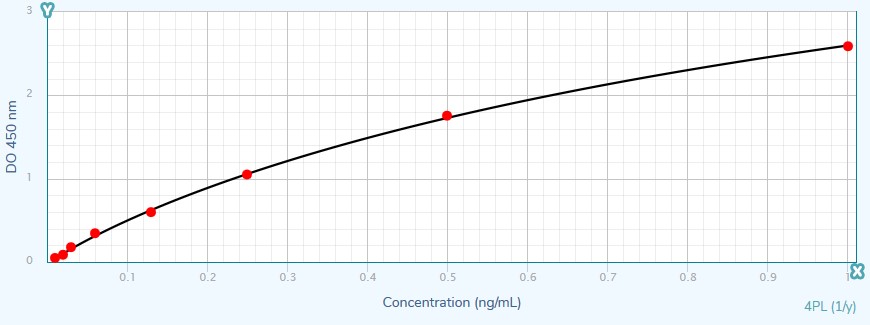
Territorial Availability: Available worldwide directly through Bertin or your local distributor
Technical Warning: Check the Additional Items Required section of this kit booklet to verify if UltraPure Water (Milli-Q or equivalent) is needed for this assay
- Synonyms
- vascular endothelial growth factor
- VEGF
- vascular permeability factor
- VPF
- Correlated keywords
- ELISA
- EIA
- angionesis
- chemotactism
- VEGF
- vascular endothelial growth factor
- vascular permeability factor
- VPF
- placental growth factor
- PLGF
- VEGF-B
- VEGF-C
- VEGF-D
- Fos-induced growth factor
- FIGF
- cystine knot
- Product Overview:
Enzyme ImmunoAssay (EIA) is a technique to detect and quantify antigens (proteins, hormones…) or antibodies in samples. It relies on the ability of an antibody to bind a specific antigen. Either the antibody or the antigen is labelled with an enzyme whose substrate is a chromogen or a fluorogen converted in a measurable product (color or fluorescence).|Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a type of EIA using a solid phase (ex: microtiter plate) coated with an antigen immobilizing the molecule to detect. Over the time, scientists have extended the term ELISA to EIAs using an antibody coating the solid phase. That explains why our EIA kits using coated antibodies are also called ELISA kits.|Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF-A or VEGF)(1), also known as vascular permeability factor (VPF)(2), has been discovered in 1983. It is a member of the VEGF family that includes in mammals placental growth factor (PLGF), VEGF-B, VEGF-C, and VEGF-D (also known as c-Fos-induced growth factor, FIGF)(1).|VEGF-A is a glycoprotein having several isoforms of 121 to 206 amino acids(1) with a molecular weight from 33 kDa to 57kDa. It is a homodimer stabilised by hydrophobic interactions and by a disulphide bound(3). The monomer structure contains a central antiparallel four-stranded β sheet with a cystine knot at the end (4).|VEGF-A is produced by many cells like fetal tissu, hematopoietic stem cells, epidermal keratinocytes, podocytes of the renal glomerulus, cardiac myocytes, prostatic epithelium, and certain epithelial cells of the adrenal cortex and lung(5). |The main function of the VEGF-A is the angionesis (formation of new capillaries from pre-existing vessels) during the embryogenesis(1) or during re-building of the blood vessel after an injury. It has also some secondary functions in the chemotacxis of macrophages/ granulocytes and in vasodilation (indirectly by NO release).|Due to its main function, overexpression of VEGF-A causes various diseases including cancer.