(+)-D-threo–PDMP (hydrochloride)
(+)-D-threo–PDMP (hydrochloride)
(+)-D-threo-PDMP is a ceramide analog and is one of the four possible stereoisomers of PDMP (Item No. 62595).{11392} (+)-D-threo-PDMP is...
€680.00 €578.00
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, causing a hyperpolarization of the membrane through the opening of a Cl- channel associated with the GABAA receptor (GABAA-R) subtype. GABAA-Rs are important therapeutic targets for a range of sedative, anxiolytic, and hypnotic agents and are implicated in several diseases including epilepsy, anxiety, depression, and substance abuse. The GABAA-R is a multimeric subunit complex. To date six ?’s, four ?’s, and four ?’s, plus alternative splicing variants of some of these subunits, have been identified. Injection in oocytes or mammalian cell lines of cRNA coding for ? and ? subunits results in the expression of functional GABAA-Rs sensitive to GABA. However, co-expression of a ? subunit is required for benzodiazepine modulation. The various effects of the benzodiazepines in brain may also be mediated via different ? subunits of the receptor. More recently there have been a number of studies demonstrating that the ? subunit of the receptor may affect subunit assembly and may also confer differential sensitivity to neurosteroids and to ethanol.
Territorial Availability: Available through Bertin Technologies only in France
| Size | 1 ea |
|---|---|
| Shipping | dry ice |
| Molecular weight | 0 |
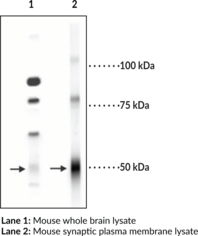
| Host | Rabbit |
| Antigen | Fusion protein from the N-terminal region of the ? subunit of rat GABAA receptor |
| Application(s) | ICC, IHC, WB |
| Formulation | 100 ?l affinity-purified antibody |
| Custom code | 3822.19 |
| UNSPSC code | 12352203 |
Cayman Chemical’s mission is to help make research possible by supplying scientists worldwide with the basic research tools necessary for advancing human and animal health. Our utmost commitment to healthcare researchers is to offer the highest quality products with an affordable pricing policy.
Our scientists are experts in the synthesis, purification, and characterization of biochemicals ranging from small drug-like heterocycles to complex biolipids, fatty acids, and many others. We are also highly skilled in all aspects of assay and antibody development, protein expression, crystallization, and structure determination.
Over the past thirty years, Cayman developed a deep knowledge base in lipid biochemistry, including research involving the arachidonic acid cascade, inositol phosphates, and cannabinoids. This knowledge enabled the production of reagents of exceptional quality for cancer, oxidative injury, epigenetics, neuroscience, inflammation, metabolism, and many additional lines of research.
Our organic and analytical chemists specialize in the rapid development of manufacturing processes and analytical methods to carry out clinical and commercial GMP-API production. Pre-clinical drug discovery efforts are currently underway in the areas of bone restoration and repair, muscular dystrophy, oncology, and inflammation. A separate group of Ph.D.-level scientists are dedicated to offering Hit-to-Lead Discovery and Profiling Services for epigenetic targets. Our knowledgeable chemists can be contracted to perform complete sample analysis for analytes measured by the majority of our assays. We also offer a wide range of analytical services using LC-MS/MS, HPLC, GC, and many other techniques.
Accreditations
ISO/IEC 17025:2005
ISO Guide 34:2009
Cayman is a leader in the field of emerging drugs of abuse, providing high-purity Schedule I-V Controlled Substances to federally-licensed laboratories and qualified academic research institutions for forensic analyses. We are certified by ACLASS Accreditation Services with dual accreditation to ISO/IEC 17025:2005 and ISO Guide 34:2009.
(+)-D-threo-PDMP is a ceramide analog and is one of the four possible stereoisomers of PDMP (Item No. 62595).{11392} (+)-D-threo-PDMP is...
The cyclopentenone prostaglandin HPLC mixture contains all of the major UV-absorbing cyclopentenone prostaglandins and their precursors supplied in methyl acetate....
Endocannabinoids, such as arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG), function as short-range modulators of cell and synaptic activity. Monoacylglycerol...
The Cayman COX Inhibitor Pack contains a combination of frequently used cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitors. Each kit contains aspirin, the archetype...
24(S),25-epoxy Cholesterol is an oxysterol and the most abundant oxysterol in mouse ventral midbrain.{43943} It activates liver X receptors (LXRs)...
This rabbit anti-mouse IgA FITC is used as the ‘secondary antibody’ for immunostaining experiments where the primary antibody is mouse...
Protein phosphorylation is an important post-translational modification that serves many key functions to regulate a protein’s activity, localization, and protein-protein...
CD34 is a transmembrane phosphoglycoprotein and sialomucin protein that is commonly used as a marker for hematopoietic progenitor cells.{59706,59704} It...
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a basic leucine zipper transcription factor encoded by NFE2L2 in humans that...
This mixture contains primary prostaglandins produced from arachidonic acid and dihomo-?-linolenic acid. Contents: Prostaglandin E1, Prostaglandin E2, Prostaglandin F1?, 6-keto...
Cytosolic PGE synthase (cPGES) is a glutathione-dependent enzyme with a predicted size of 18.6 kDa (23 kDa on SDS-PAGE). The...
Secretory phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) (Type IIA) is a calcium-dependent PLA2 superfamily member that is encoded by PLA2G2A in humans.{56210} It...
Proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9 (PCSK9) is a member of the subtilisin serine protease family with an important role in...
This mixture contains the primary COX products produced by most mammalian tissues. Contents: Prostaglandin D2, Prostaglandin E2, 6-keto Prostaglandin F1?,...
This mixture contains the characteristic metabolites of both PGI2 and TXA2. Contents: Thromboxane B2, 11-dehydro Thromboxane B2, 6-keto Prostaglandin F1?,...
GST-tag Polyclonal Antibody (FITC) is a probe for the immunochemical detection of GST tags on recombinant proteins. Recombinant proteins are...
This mixture contains the primary metabolites of prostaglandins (PGs) D2, E2, and F2?. Contents: 13,14-dihydro-15-keto PGD2, 13,14-dihydro-15-keto PGE2, 11?-PGF2?, 13,14-dihydro-15-keto...
GPR17 is a G protein-coupled receptor that has been identified as a dualistic receptor recognizing signals from two unrelated chemical...
Headquarters:
Parc d’activités du Pas du Lac
10 bis avenue Ampère
78180 Montigny le Bretonneux
France
Copyright © 2024 BERTIN BIOREAGENT. All rights reserved | Terms & conditions