Territorial Availability: Available through Bertin Technologies only in France
- Correlated keywords
- METTL 3 14 m6-A ETV6 RUNX1 ETV-6 RUNX-1-(E/R) MTA70 Methyl-transferase n-6 selfrenewal post-natal Noncatalytic
- Product Overview:
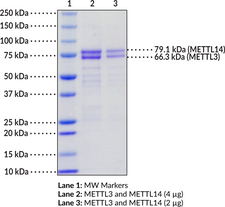
Methyltransferase-like protein 3 (METTL3) and METTL14 are m6A RNA methyltransferases encoded by the METTL3 and METTL14 genes, respectively, in humans.{50138} METTL3 and METTL14 form a stable complex in the cytoplasm then localize to the nucleus via a METTL3 nuclear localization sequence. METTL3 contains an N-terminal leader helix domain that interacts with Wilms’ tumor 1-associated protein (WTAP) in the nucleus, which confers localization of the complex to nuclear speckles. METTL14 contains a C-terminal arginine-glycine-glycine (RGG) sequence that contributes to the catalytic activity of the complex. METTL3 and METTL14 each contain methyltransferase domains but the METTL3 domain alone binds S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) or S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) while METTL14 interacts with RNA.{45519} The METTL3/14 complex primarily binds to regions of RNA that correspond to intergenic and intron regions of DNA, and it preferentially methylates RNA substrates that contain the sequence GGACU, with little preference for secondary structural features of the substrates.{45520} METTL3 and METTL14 are involved in hematopoietic stem cell differentiation in vitro and are necessary for self-renewal and reconstitution of hematopoietic stem cells following bone marrow transplantation in mice.{45521} Mettl3 knockdown or Mettl14 knockout increases radial glia cell cycle length in embryonic mouse brain, and Mettl14 knockout extends cortical neurogenesis into the postnatal period.{45523} Knockdown of METTL3 or METTL14 also increases proliferation of glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs) in vitro and increases tumor size in a mouse orthotopic model using GSCs.{45524} The expression of METTL3 and METTL14 is reduced in juvenile patients with ETV6/RUNX1(E/R)-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).{45522}
Cayman Chemical’s mission is to help make research possible by supplying scientists worldwide with the basic research tools necessary for advancing human and animal health. Our utmost commitment to healthcare researchers is to offer the highest quality products with an affordable pricing policy.
Our scientists are experts in the synthesis, purification, and characterization of biochemicals ranging from small drug-like heterocycles to complex biolipids, fatty acids, and many others. We are also highly skilled in all aspects of assay and antibody development, protein expression, crystallization, and structure determination.
Over the past thirty years, Cayman developed a deep knowledge base in lipid biochemistry, including research involving the arachidonic acid cascade, inositol phosphates, and cannabinoids. This knowledge enabled the production of reagents of exceptional quality for cancer, oxidative injury, epigenetics, neuroscience, inflammation, metabolism, and many additional lines of research.
Our organic and analytical chemists specialize in the rapid development of manufacturing processes and analytical methods to carry out clinical and commercial GMP-API production. Pre-clinical drug discovery efforts are currently underway in the areas of bone restoration and repair, muscular dystrophy, oncology, and inflammation. A separate group of Ph.D.-level scientists are dedicated to offering Hit-to-Lead Discovery and Profiling Services for epigenetic targets. Our knowledgeable chemists can be contracted to perform complete sample analysis for analytes measured by the majority of our assays. We also offer a wide range of analytical services using LC-MS/MS, HPLC, GC, and many other techniques.
Accreditations
ISO/IEC 17025:2005
ISO Guide 34:2009
Cayman is a leader in the field of emerging drugs of abuse, providing high-purity Schedule I-V Controlled Substances to federally-licensed laboratories and qualified academic research institutions for forensic analyses. We are certified by ACLASS Accreditation Services with dual accreditation to ISO/IEC 17025:2005 and ISO Guide 34:2009.