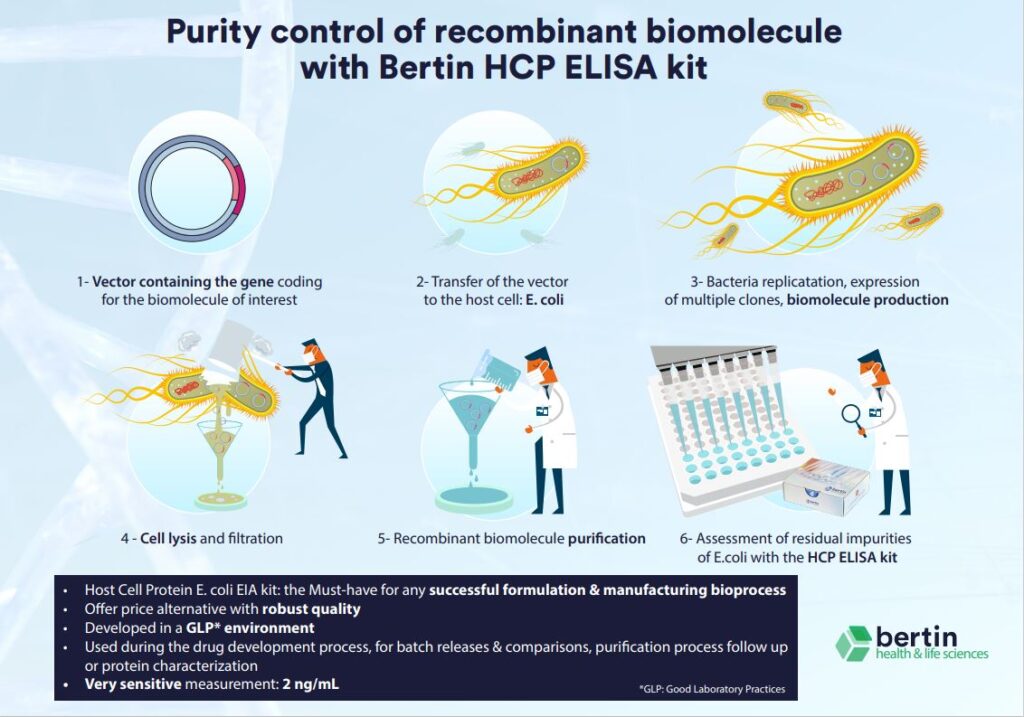
Host cell proteins (HCPs) refer to proteins that are either produced or encoded by the host organisms utilized in the manufacturing of recombinant therapeutic proteins.
To meet clinical standards, biopharmaceuticals must be devoid of impurities related to the production process. The elimination of HCPs is a major challenge in the production of biopharmaceuticals. HCPs, being the principal type of process-related impurities, are undesirable in the purified protein product as they are believed to pose a risk to patient safety. HCPs may exhibit biological activity in the human body or, in the case of HCPs with protease activity, affect the stability of the product by degrading either the therapeutic protein itself or product-stabilizing additives.
The development of HCP detection methods is a significant advancement towards detecting residual contamination during bioprocessing and the final biopharmaceutical product. Over time, several approaches have been established to detect HCPs. To detect small amounts of HCPs, a highly sensitive and specific analytical method is required. Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assays (ELISA) are user-friendly in routine analysis and can quantify low levels of HCPs. With the Bertin Bioreagent HCP ELISA kit, researchers can reliably assess relative quantities of E. coli HCP in manufactured or research bioproducts.