Biophysical characterization methods such as surface plasmon resonance (SPR) are powerful tools for characterizing molecular interactions and binding mechanisms, including antibody-antigen, protein-drug and protein-protein interactions.
When used to analyze antibody-antigen interactions, SPR data can help scientists select antibodies with optimal characteristics for their specific applications. The equilibrium dissociation constant (KD), for example, can be used to assess antibody affinity and sensitivity.
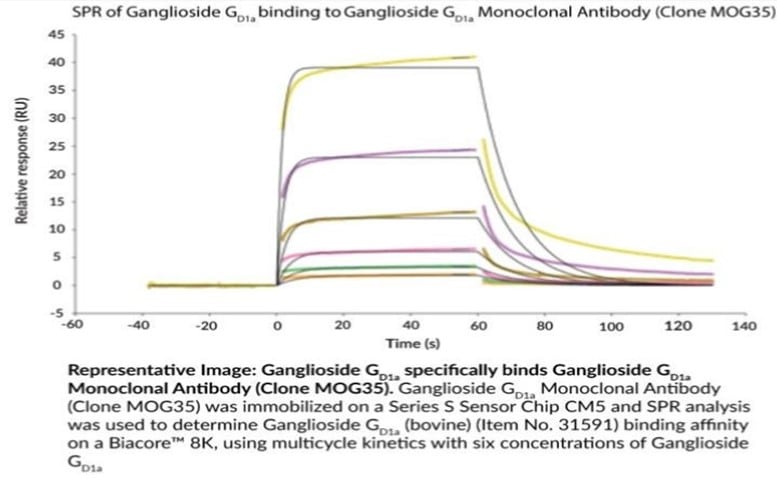
Recently, Cayman scientists used the SPR method to characterize the binding kinetics and affinities of several of their anti-ganglioside monoclonal antibodies with their respective antigens using Biacore technologies:
| Monoclonal Antibody | Clone | Antigene | KD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ganglioside GD1a | MOG35 | Ganglioside GD1a (bovine brain) (sodium salt) | 2.01 μM | 38295 |
| Ganglioside GD1a | TBG3 | Ganglioside GD1a (bovine brain) (sodium salt) | 1.36 μM | 38296 |
| Ganglioside GD1b | MOG1 | Ganglioside GD1b (porcine) (sodium salt) | 0.052 μM | 38293 |
| Ganglioside GM1 | DG2 | Ganglioside GM1 (porcine brain) (sodium salt) | 1.81 μM | 38290 |
| Ganglioside GQ1b | CGM3 | Ganglioside GQ1b Mixture (sodium salt) | 8.18 μM | 38287 |