TAF 10 Peptide
TAF 10 Peptide
TAF10 is one of many protein factors or coactivators associated with RNA polymerase II activity.{16903} One vial of this peptide...
€465.00
Enzyme ImmunoAssay (EIA) is a technique to detect and quantify antigens (proteins, hormones…) or antibodies in samples. It relies on the ability of an antibody to bind a specific antigen. Either the antibody or the antigen is labelled with an enzyme whose substrate is a chromogen or a fluorogen converted in a measurable product (color or fluorescence).|Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a type of EIA using a solid phase (ex: microtiter plate) coated with an antigen immobilizing the molecule to detect. Over the time, scientists have extended the term ELISA to EIAs using an antibody coating the solid phase. That explains why our EIA kits using coated antibodies are also called ELISA kits.|IL-8 is a polypeptide of 72-77 amino acids(1), known also as CXCL8, GCP-1 and NAP-1. Member of the CXC chemokine family, it can adopt a monomeric or homodimeric conformation containing a triple-stranded anti-parallel beta-sheet arranged in a Greek key and a long C-terminal helix(2). IL-8 could also form a heterodimer with PF4 activity(3). The receptors of IL-8 are CXCR1 and CXCR2(4).|IL-8 is mainly produced by macrophages(5). It acts as an angiogenic factor in human microvascular endothelial cells(6). The main role of IL-8 in inflammation is the recruitment of neutrophils(7), although it is also responsible for the chemotactic migration and activation of monocytes, lymphocytes, basophils, and eosinophils at sites of inflammation(8).
Territorial Availability: Available worldwide directly through Bertin or your local distributor
Technical Warning: Check the Additional Items Required section of this kit booklet to verify if UltraPure Water (Milli-Q or equivalent) is needed for this assay
| Size | 96 wells |
|---|---|
| Shipping | wet ice |
| Specificity | refer to technical booklet |
| Application media | It is the responsibility of the user to check the compatibility of the assay with the study matrix |
| Sample volume | 100 µL |
| Tracer | horseradish peroxidase HRP |
| Detection limit | |
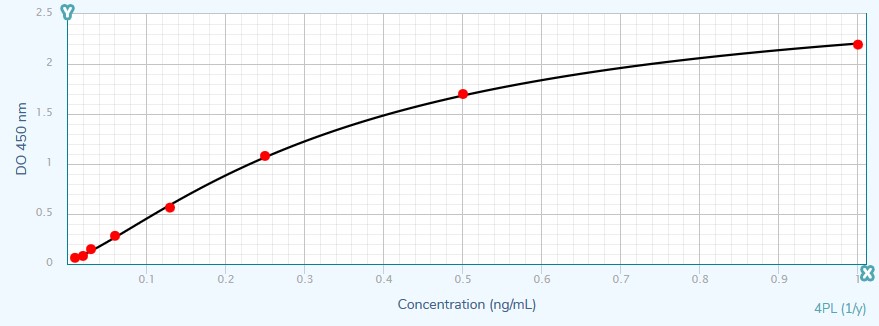
| Standard Curve Range | 0,01-1,00 ng/mL |
| Custom code | 3822000000 |
| UNSPSC code | 41116104 |
TAF10 is one of many protein factors or coactivators associated with RNA polymerase II activity.{16903} One vial of this peptide...
Prostaglandin I synthase (PGIS) catalyzes the isomerization of PGH2 to PGI2. PGI2 (prostacyclin) is a potent vasodilator and inhibitor of...
Histone H2A is a core histone that forms a dimer with histone H2B.{46631} Two histone H2A/H2B dimers form an octameric...
This mixture contains primary prostaglandins produced from arachidonic acid and dihomo-?-linolenic acid. Contents: Prostaglandin E1, Prostaglandin E2, Prostaglandin F1?, 6-keto...
The Cayman COX Inhibitor Pack contains a combination of frequently used cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitors. Each kit contains aspirin, the archetype...
Sirtuin 5 (SIRT5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the NAD-dependent removal of malonyl, succinyl, and glutaryl groups from target proteins.{55107,55108}...
Inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 (IP6K2) is a cytoplasmic kinase that catalyzes the conversion of IP6 to diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate in the...
Platelet-activating factor (PAF) is an important lipid mediator involved in inflammation. PAF-acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH) is an extracellular phospholipase A2 which hydrolyzes...
Programmed cell death protein 4 (PDCD4) levels are elevated during apoptosis and absent in many cancer samples.{16340,16167} Loss of PDCD4...
To be used in conjunction with Cayman’s NAPE-PLD polyclonal antibody (aa 6-20) (Item No. 10306) to block protein-antibody complex formation...
The cyclopentenone prostaglandin HPLC mixture contains all of the major UV-absorbing cyclopentenone prostaglandins and their precursors supplied in methyl acetate....
This mixture contains the primary COX products produced by most mammalian tissues. Contents: Prostaglandin D2, Prostaglandin E2, 6-keto Prostaglandin F1?,...
This mixture contains the primary metabolites of prostaglandins (PGs) D2, E2, and F2?. Contents: 13,14-dihydro-15-keto PGD2, 13,14-dihydro-15-keto PGE2, 11?-PGF2?, 13,14-dihydro-15-keto...
To be used in conjunction with Cayman’s FABP3 polyclonal antibody (Catalog No. 10233) to block protein-antibody complex formation during immunochemical...
Amyloid-? (1-8, A2V) is a truncated form of amyloid-? (A?) that contains a valine to alanine substitution at position 2...
Proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9 (PCSK9) is a member of the subtilisin serine protease family with an important role in...
This mixture contains the characteristic metabolites of both PGI2 and TXA2. Contents: Thromboxane B2, 11-dehydro Thromboxane B2, 6-keto Prostaglandin F1?,...
GST-tag Polyclonal Antibody (FITC) is a probe for the immunochemical detection of GST tags on recombinant proteins. Recombinant proteins are...
Headquarters:
Parc d’activités du Pas du Lac
10 bis avenue Ampère
78180 Montigny le Bretonneux
France
Copyright © 2024 BERTIN BIOREAGENT. All rights reserved | Terms & conditions